How To Create Function In Mysql Example
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to create stored functions using the CREATE FUNCTION statement.
A stored function is a special kind stored program that returns a single value. Typically, you use stored functions to encapsulate common formulas or business rules that are reusable among SQL statements or stored programs.
Different from a stored procedure, you can use a stored function in SQL statements wherever an expression is used. This helps improve the readability and maintainability of the procedural code.
To create a stored function, you use the CREATE FUNCTION statement.
MySQL CREATE FUNCTION syntax
The following illustrates the basic syntax for creating a new stored function:
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql )
DELIMITER $$ CREATE FUNCTION function_name( param1, param2,… ) RETURNS datatype [NOT] DETERMINISTIC BEGIN -- statements END $$ DELIMITER ;
In this syntax:
First, specify the name of the stored function that you want to create after CREATE FUNCTION keywords.
Second, list all parameters of the stored function inside the parentheses followed by the function name. By default, all parameters are the IN parameters. You cannot specify IN , OUT or INOUT modifiers to parameters
Third, specify the data type of the return value in the RETURNS statement, which can be any valid MySQL data types.
Fourth, specify if a function is deterministic or not using the DETERMINISTIC keyword.
A deterministic function always returns the same result for the same input parameters whereas a non-deterministic function returns different results for the same input parameters.
If you don't use DETERMINISTIC or NOT DETERMINISTIC, MySQL uses the NOT DETERMINISTIC option by default.
Fifth, write the code in the body of the stored function in the BEGIN END block. Inside the body section, you need to specify at least one RETURN statement. The RETURN statement returns a value to the calling programs. Whenever the RETURN statement is reached, the execution of the stored function is terminated immediately.
MySQL CREATE FUNCTION example
Let's take the example of creating a stored function. We will use the customers table in the sample database for the demonstration.
The following CREATE FUNCTION statement creates a function that returns the customer level based on credit:
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql )
DELIMITER $$ CREATE FUNCTION CustomerLevel( credit DECIMAL(10,2) ) RETURNS VARCHAR(20) DETERMINISTIC BEGIN DECLARE customerLevel VARCHAR(20); IF credit > 50000 THEN SET customerLevel = 'PLATINUM'; ELSEIF (credit >= 50000 AND credit <= 10000) THEN SET customerLevel = 'GOLD'; ELSEIF credit < 10000 THEN SET customerLevel = 'SILVER'; END IF; -- return the customer level RETURN (customerLevel); END$$ DELIMITER ;
Once the function is created, you can view it in MySQL Workbench under the Functions section:
Or you can view all stored functions in the current classicmodels database by using the SHOW FUNCTION STATUS as follows:
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql )
SHOW FUNCTION STATUS WHERE db = 'classicmodels';

Calling a stored function in an SQL statement
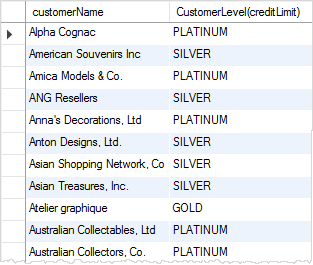
The following statement uses the CustomerLevel stored function:
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql )
SELECT customerName, CustomerLevel(creditLimit) FROM customers ORDER BY customerName;
Calling a stored function in a stored procedure
The following statement creates a new stored procedure that calls the CustomerLevel() stored function:
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql )
DELIMITER $$ CREATE PROCEDURE GetCustomerLevel( IN customerNo INT, OUT customerLevel VARCHAR(20) ) BEGIN DECLARE credit DEC(10,2) DEFAULT 0; -- get credit limit of a customer SELECT creditLimit INTO credit FROM customers WHERE customerNumber = customerNo; -- call the function SET customerLevel = CustomerLevel(credit); END$$ DELIMITER ;
The following illustrates how to call the GetCustomerLevel() stored procedure:
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql )
CALL GetCustomerLevel(-131,@customerLevel); SELECT @customerLevel;
It's important to notice that if a stored function contains SQL statements that query data from tables, then you should not use it in other SQL statements; otherwise, the stored function will slow down the speed of the query.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to create a stored function to encapsulate the common formula or business rules.
Was this tutorial helpful?
How To Create Function In Mysql Example
Source: https://www.mysqltutorial.org/mysql-stored-function/
Posted by: rodriguezalmou1981.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Create Function In Mysql Example"
Post a Comment